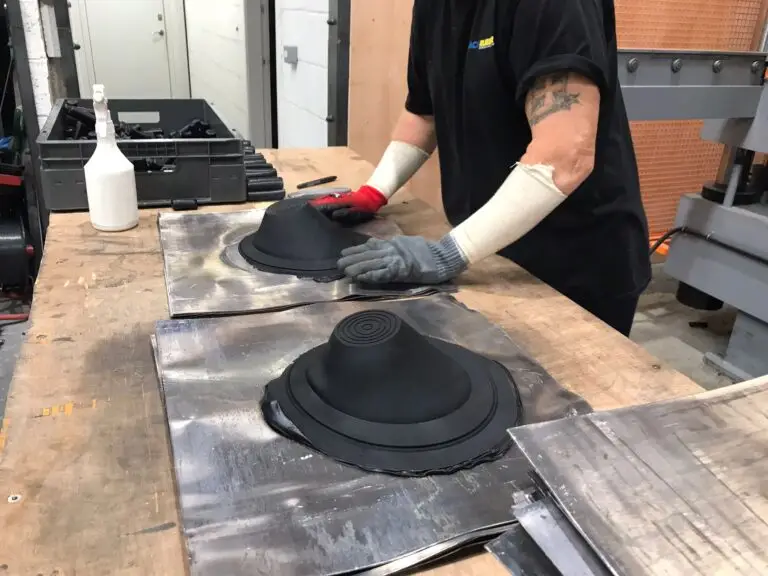
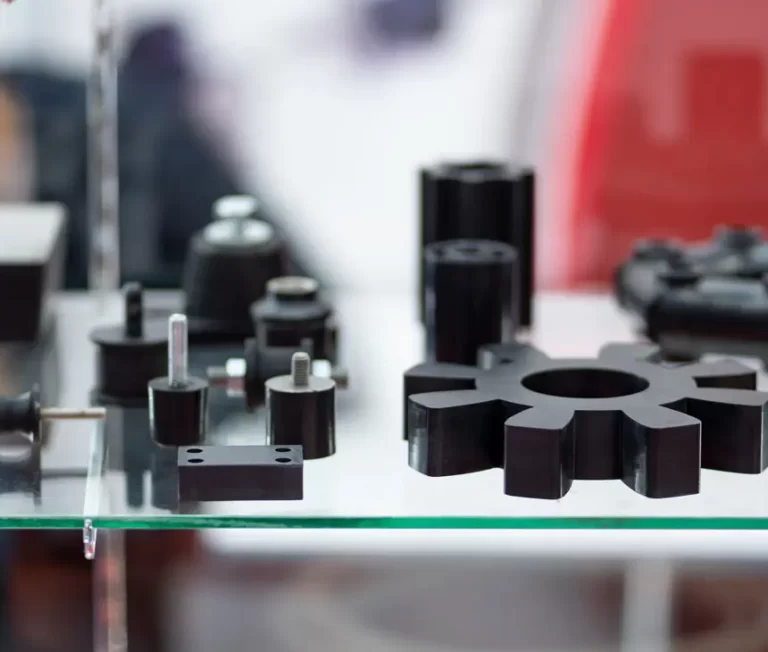
In the dynamic realm of manufacturing, the rubber moulding industry stands at the forefront of innovation. In this article, we delve into the latest trends reshaping the rubber moulding landscape, uncovering transformative changes that promise to redefine the industry’s future.
Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing: Transforming Rubber Moulding Processes
The infusion of Industry 4.0 principles has revolutionized the rubber moulding arena. Smart manufacturing, driven by data and connectivity, has not only streamlined production but also introduced predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and costs.
3D Printing Revolutionizes Rubber Molding: A Paradigm Shift
The marriage of 3D printing and rubber moulding has opened new doors for design flexibility and prototyping. Additive manufacturing enables the creation of intricate molds with greater precision and speed, reducing lead times. This trend is particularly beneficial for customized or low-volume production, where traditional molding methods might be less cost-effective.
Advanced Materials for Enhanced Performance
Innovation extends to the materials used in rubber moulding. New formulations and combinations are emerging, offering enhanced properties such as improved durability, flexibility, and resistance to extreme conditions. From high-performance elastomers to eco-friendly compounds, these materials are meeting the diverse needs of industries ranging from automotive to healthcare.
Robotics and Automation in Moulding Processes
Automation has become a cornerstone in modern manufacturing, and rubber moulding is no exception. Robots are now handling tasks that were once labor-intensive, such as the precise placement of materials and the removal of finished products from moulds. This not only increases efficiency but also ensures a higher level of consistency in the final products.
Conclusion
As we witness these groundbreaking trends in rubber molding technology, it’s evident that the industry is on the brink of a new era. From smart manufacturing to 3D printing and advanced materials, each innovation brings us closer to a future where rubber products are not just manufactured but crafted with unparalleled precision and efficiency. The journey towards excellence in rubber moulding continues, promising exciting possibilities for industries and consumers alike.